Apache Beam allows one to create reusable, chainable pipelines for data processing tasks. While it is possible to run BEAM python jobs directly using the DirectRunner without a backend, in production environments, we tend to use a backend runner such as Spark or Flink.
This article will try to explain how to setup and run a local Flink cluster to run BEAM jobs on. There are two different scenarios: running Flink through a set of Docker containers; and running Flink on a local kubernetes cluster. This article will explain and demonstrate how to do so using Docker. A subsequent article will go into detail on how to deploy a Flink cluster in Kubernetes using Kind cluster locally.
The main components of a Flink cluster are:
-
Job Manager
The core component of a Flink cluster. It serves as the control plane of the cluster and coordinates work submitted to the cluster.
-
Task Manager
Component that performs / executes the work of a Flink job from the Job Manager.
Out of the box, Flink supports pipelines written in Java. For other languages such as Python or Go LANG, we need to submit the job as a PortableRunner.
This requires running 2 additional components:
-
Job Server
This is where the pipeline gets submitted from the Python SDK via the Job API. Beam converts it to Runner API before submitting the pipeline via Job API to Beam’s job server.
The Job Server translates the pipeline code into a compatible Flink program and submits it to the Flink cluster for execution.
The compiled pipeline code is a Flink program that contains an
ExecutableStagetransform, which is a ParDo transform designed for holding language dependent code. -
Python SDK Harness
This is the language specific environment where the target pipeline is executed after its submitted to the Flink cluster.
When Flink executes Python code, it sends data to the Python environment containing the Python SDK harness.
An example docker compose config for running Flink cluster locally in session mode:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
version: "3.9"
volumes:
flink-job-artifacts:
name: flink-job-artifacts
services:
jobmanager:
image: flink:1.15.2
expose:
- "6123"
- "6124"
ports:
- "8081:8081"
command: jobmanager
volumes:
- ./conf:/opt/flink/conf
- /tmp/flink-checkpoints-directory:/tmp/flink-checkpoints-directory
- /tmp/flink-savepoints-directory:/tmp/flink-savepoints-directory
environment:
- JOB_MANAGER_RPC_ADDRESS=localhost
network_mode: host
taskmanager:
image: flink:1.15.2
expose:
- "6121"
- "6122"
- "6125"
depends_on:
- jobmanager
command: taskmanager
scale: 1
volumes:
- ./conf:/opt/flink/conf
- /tmp/flink-checkpoints-directory:/tmp/flink-checkpoints-directory
- /tmp/flink-savepoints-directory:/tmp/flink-savepoints-directory
- flink-job-artifacts:/artifacts:rw
- ../outputs:/outputs:rw # mounts local output dir
environment:
- JOB_MANAGER_RPC_ADDRESS=localhost
network_mode: host
# BEAM Job Server
# e.g. if pip apache-beam == 2.41.0, the image must be the same
jobserver:
image: apache/beam_flink1.15_job_server:2.41.0
ports:
- "8099:8099"
volumes:
- flink-job-artifacts:/artifacts:rw
- ../data:/data:rw # data source from localhost
- ../outputs:/outputs:rw # mounts local output dir
command: [
"--artifacts-dir",
"/artifacts",
"--flink-master-url",
"localhost:8081",
"--clean-artifacts-per-job",
"true"
]
network_mode: host
# Specifies a python runner environment
# SDK tag version must match the pip installed apache-beam version
# e.g. if pip apache-beam == 2.41.0, the image must be the same
python_sdk:
image: apache/beam_python3.8_sdk:2.41.0
depends_on:
- jobmanager
- taskmanager
container_name: beam-python-sdk
command: --worker_pool
ports:
- "50000:50000"
volumes:
- flink-job-artifacts:/artifacts:rw
- ../data:/data:rw # data source from localhost
- ../outputs:/outputs:rw # mounts local output dir
network_mode: host
We declare a volumes of flink-job-artifacts store the output of the translated pipeline before submission to the Flink server. Both the taskmanager and job server must share the same path in order for the taskmanager to pick up the compiled pipeline.
Next we run a job server where the actual BEAM code is submitted to.
Note that the version of apache-beam installed locally in pip must match that of the sdk and job server. e.g. if we have python 3.8 and apache-beam==2.41.0 installed locally, we need the apache/beam_flink1.15_job_server:2.41.0 and apache/beam_python3.8_sdk:2.41.0 images.
Note that we are using the network_mode: host, which means it uses the underlying host’s network settings rather than the docker engine. This is required for the various services to communicate as there is no service discovery and the urls are hardcoded to localhost within the Flink JAR files.
The above cluster runs in session mode which means we can have multiple task managers by increasing the scale parameter.
To run:
1
docker compose -f docker-compose-portable.yml up
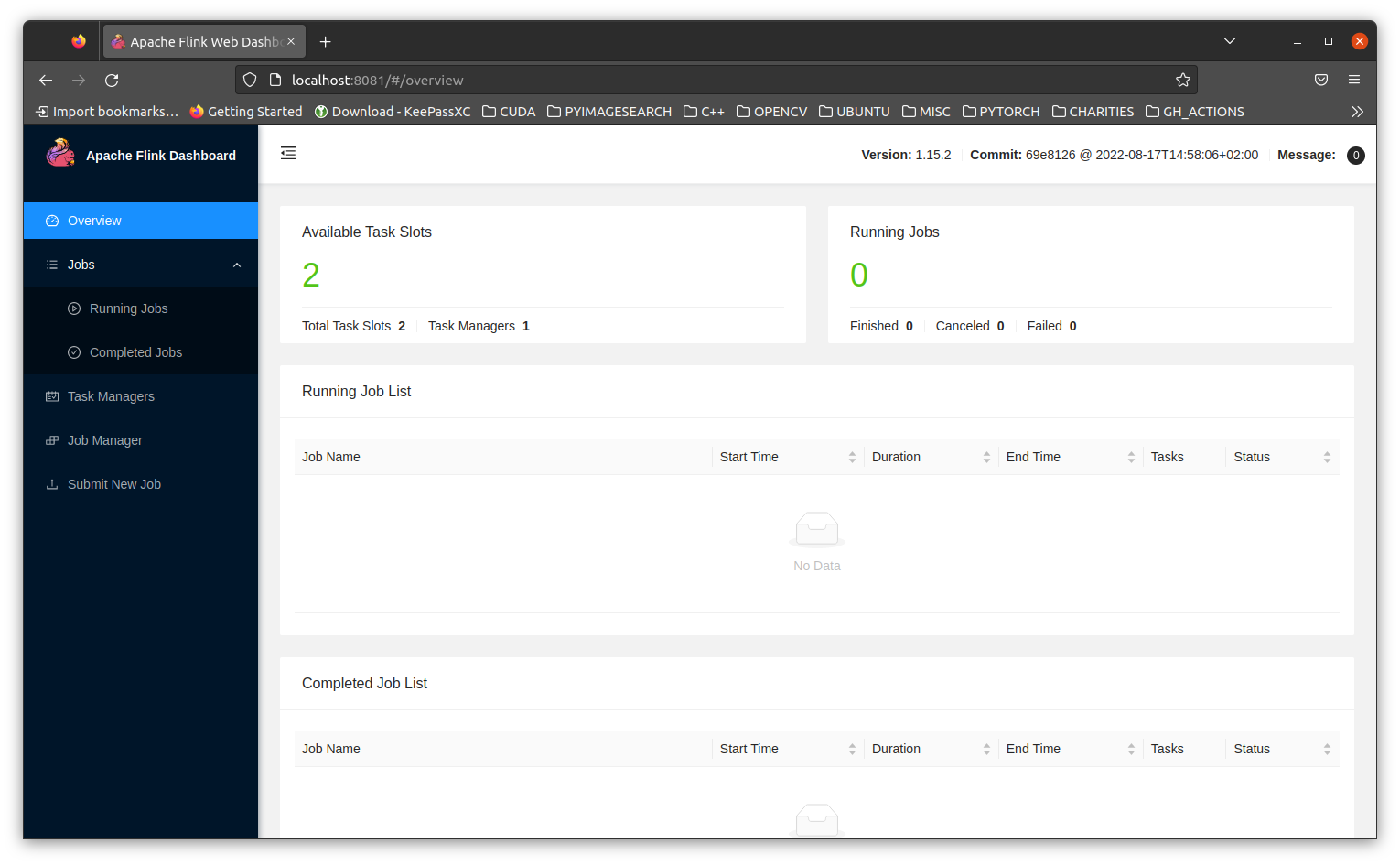
Check that the console is running by going to localhost:8081
We can create a simple Beam python pipeline like below to test:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import logging
import argparse
import apache_beam as beam
from apache_beam.io import ReadFromText
from apache_beam.io import WriteToText
from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import PipelineOptions
def run():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--output", help="Path to save output")
known_args, pipeline_args = ap.parse_known_args()
pipeline_options = PipelineOptions(pipeline_args)
with beam.Pipeline(options=pipeline_options) as p:
(p
| 'Create words' >> beam.Create(['to be or not to be'])
| 'Split words' >> beam.FlatMap(lambda words: words.split(' '))
| 'Write to file' >> WriteToText(known_args.output)
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
run()
Without going into how BEAM works, which is left as an exercise to the reader, the above pipeline creates an initial string which is passed to a transform that splits up the words, and finally to another transform that writes the words into a file sink.
The pipeline options are also created via the argparse lib. Structuring the pipeline above allows for running locally in dev mode using DirectRunner and also PortableRunner
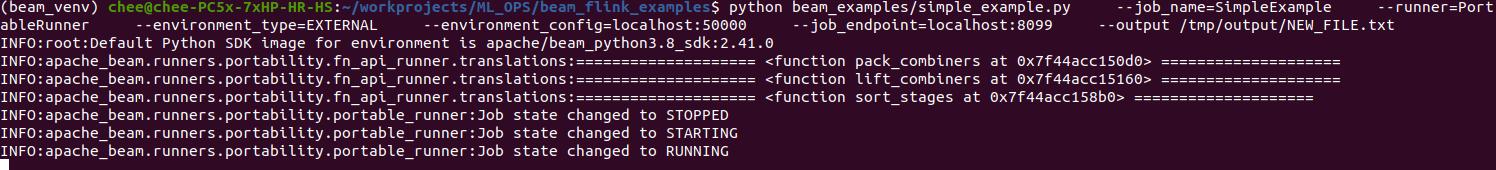
To run the above pipeline:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
python beam_examples/simple_example.py \
--job_name=SimpleExample \
--runner=PortableRunner \
--environment_type=EXTERNAL \
--environment_config=localhost:50000 \
--job_endpoint=localhost:8099 \
--output /outputs/NEW_FILE.txt
You can also view the job progress via the dashboard
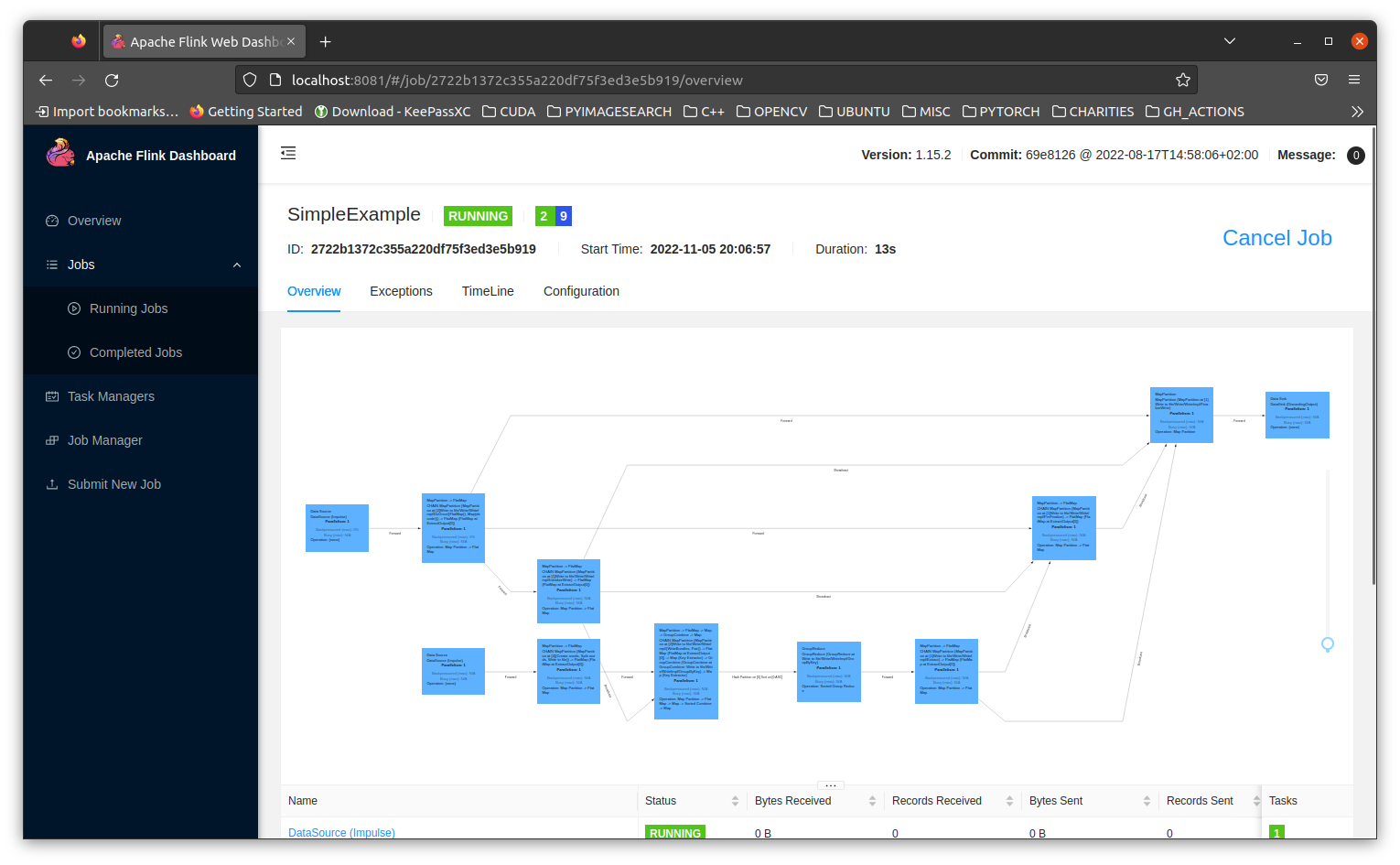
Note that the job_endpoint is set to the job server service defined in the above compose config. The environment_config refers to the python-sdk which is attached at port 50000 to the task manager.
The above example has mounted a local directory of ../outputs to store the results of the pipeline.